| Gene Symbol | JJJ1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 855495 |
| Full Name | Jjj1p |
| Gene Type | protein-coding |
| Organism | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C |
HOME
ORF » Species Summary » Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C » JJJ1 cDNA ORF clone
| Gene Symbol | JJJ1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 855495 |
| Full Name | Jjj1p |
| Gene Type | protein-coding |
| Organism | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C |
| mRNA | Protein | Name |
|---|---|---|
| NM_001183065.1 | NP_014172.1 | Jjj1p |

| Gallus gallus (chicken) | DNAJC21 | XP_425006.2 |
| Danio rerio (zebrafish) | dnajc21 | NP_956338.1 |
| Xenopus tropicalis (tropical clawed frog) | dnajc21 | XP_004910484.1 |
| Homo sapiens (human) | DNAJC21 | NP_919259.3 |
| Bos taurus (cattle) | DNAJC21 | NP_001179147.1 |
| Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) | CG2790 | NP_611986.2 |
| Eremothecium gossypii | AGOS_ABL194C | NP_982753.1 |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | Dnajc21 | NP_084322.2 |
| Anopheles gambiae (African malaria mosquito) | AgaP_AGAP009943 | XP_319073.4 |
| Caenorhabditis elegans (roundworm) | dnj-17 | NP_499759.1 |
| Kluyveromyces lactis | KLLA0D19602g | XP_453932.1 |
| Pan troglodytes (chimpanzee) | DNAJC21 | XP_003310804.1 |
| Canis lupus familiaris (dog) | DNAJC21 | XP_005619457.1 |
| Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) | Dnajc21 | NP_620211.2 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast) | JJJ1 | NP_014172.1 |

The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XIV and its evolutionary implications.
Philippsen P, Kleine K, P?hlmann R, D?sterh?ft A, Hamberg K, Hegemann JH, Obermaier B, Urrestarazu LA, Aert R, Albermann K, Altmann R, Andr? B, Baladron V, Ballesta JP, B?cam AM, Beinhauer J, Boskovic J, Buitrago MJ, Bussereau F, Coster F, Crouzet M, D'Angelo M, Dal Pero F, De Antoni A, Del Rey F, Doignon F, Domdey H, Dubois E, Fiedler T, Fleig U, Floeth M, Fritz C, Gaillardin C, Garcia-Cantalejo JM, Glansdorff NN, Goffeau A, Gueldener U, Herbert C, Heumann K, Heuss-Neitzel D, Hilbert H, Hinni K, Iraqui Houssaini I, Jacquet M, Jimenez A, Jonniaux JL, Karpfinger L, Lanfranchi G, Lepingle A, Levesque H, Lyck R, Maftahi M, Mallet L, Maurer KC, Messenguy F, Mewes HW, M?sti D, Nasr F, Nicaud JM, Niedenthal RK, Pandolfo D, Pi?rard A, Piravandi E, Planta RJ, Pohl TM, Purnelle B, Rebischung C, Remacha M, Revuelta JL, Rinke M, Saiz JE, Sartorello F, Scherens B, Sen-Gupta M, Soler-Mira A, Urbanus JH, Valle G, Van Dyck L, Verhasselt P, Vierendeels F, Vissers S, Voet M, Volckaert G, Wach A, Wambutt R, Wedler H, Zollner A, Hani J
Nature387(6632 Suppl)93-8(1997 May)
Life with 6000 genes.
Goffeau A, Barrell BG, Bussey H, Davis RW, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel JD, Jacq C, Johnston M, Louis EJ, Mewes HW, Murakami Y, Philippsen P, Tettelin H, Oliver SG
Science (New York, N.Y.)274(5287)546, 563-7(1996 Oct)
GeneRIFs: Gene References Into Functions What's a GeneRIF?
biochemically characterized ribosomal complexes of the yeast 60S-biogenesis factor Arx1 and late-maturation factors Rei1 and Jjj1 and determined their cryo-EM structures
Title: Cryo-EM structures of Arx1 and maturation factors Rei1 and Jjj1 bound to the 60S ribosomal subunit.
Jjj1 and Zuo1, function together with their partner Hsp70 proteins to mediate the biogenesis of ribosomes themselves. Jjj1 and Zuo1 have overlapping but distinct functions in this complex process
Title: A ribosome-anchored chaperone network that facilitates eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis.
both Rei1 and Jjj1 are required for dissociation of Arx1 from the pre-60 S subunit, and the region of Jjj1 that mediates interaction with Rei1 is required in vivo for 60 S subunit biogenesis
Title: The cytosolic J-protein, Jjj1, and Rei1 function in the removal of the pre-60 S subunit factor Arx1.
Preferentially required for the release of pre-ribosomal shuttling factors Arx1 and Alb1 from the cytoplasmic pre-60S particles.
Title: The Hsp40 chaperone Jjj1 is required for the nucleo-cytoplasmic recycling of preribosomal factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Jjj1, when overexpressed, is able to partially substitute for the Zuo1:Ssb chaperone machinery by recruiting Ssa to the ribosome, facilitating its interaction with nascent polypeptide chains
Title: The specialized cytosolic J-protein, Jjj1, functions in 60S ribosomal subunit biogenesis.
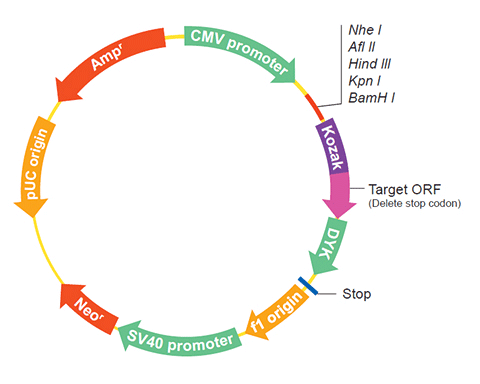
The following JJJ1 gene cDNA ORF clone sequences were retrieved from the NCBI Reference Sequence Database (RefSeq). These sequences represent the protein coding region of the JJJ1 cDNA ORF which is encoded by the open reading frame (ORF) sequence. ORF sequences can be delivered in our standard vector, pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK or the vector of your choice as an expression/transfection-ready ORF clone. Not the clone you want? Click here to find your clone.
| CloneID | OSi04420 | |
| Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) | NM_001183065.1 | |
| Accession Version | NM_001183065.1 Latest version! | Documents for ORF clone product in default vector |
| Sequence Information | ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 1773bp) Protein sequence SNP |
|
| Vector | pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector |  User Manual User Manual |
| Clone information | Clone Map |  MSDS MSDS |
| Tag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK | C terminal DYKDDDDK tags | |
| ORF Insert Method | CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology | |
| Insert Structure | linear | |
| Update Date | 2019-10-31 | |
| Organism | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | |
| Product | Jjj1p | |
| Comment | Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by SGD. This record is derived from an annotated genomic sequence (NC_001146). ##Genome-Annotation-Data-START## Annotation Provider :: SGD Annotation Status :: Full Annotation Annotation Version :: R64-2-1 URL :: http://www.yeastgenome.org/ ##Genome-Annotation-Data-END## COMPLETENESS: incomplete on both ends. | |
1 | ATGAAGACCT GCTACTATGA GCTTTTAGGG GTCGAAACGC ATGCTTCTGA TCTTGAGTTA |
The stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
| RefSeq | NP_014172.1 |
| CDS | 1..1773 |
| Translation |

Target ORF information:
Target ORF information:
|
 NM_001183065.1 NM_001183065.1 |

1 | ATGAAGACCT GCTACTATGA GCTTTTAGGG GTCGAAACGC ATGCTTCTGA TCTTGAGTTA |
The stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XIV and its evolutionary implications. |
Life with 6000 genes. |