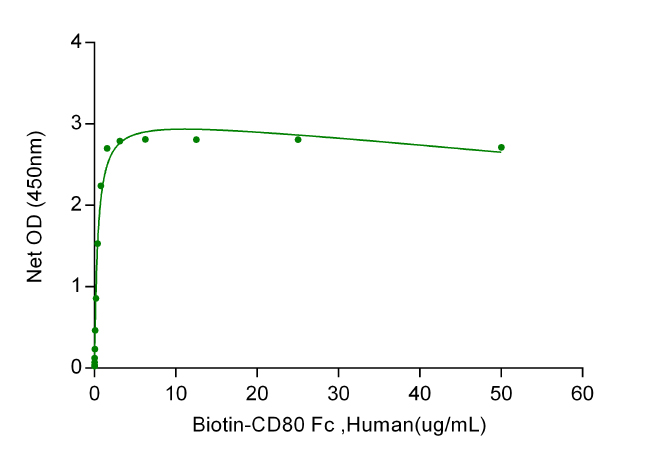
Immobilized human CD28 Fcat 2μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind human Biotin-B7-1(CD80) Fc with a linear range of 0.01-0.5μg/mL.
CD28 Fc Chimera, Human
Human CD28 is composed of four exons encoding a protein of 220 amino acids that is expressed on the cell surface as a glycosylated, disulfide-linked homodimer of 44 kDa. Members of the CD28 family share a number of common features. These receptors consist of paired V-set immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) domains attached to single transmembrane domains and cytoplasmic domains that contain critical signaling motifs. The CD28 and CTLA4 ligands, CD80 and CD86, consist of single V-set and C1-set IgSF domains. The interaction of these costimulatory receptors with ligands is mediated through the MYPPPY motif within the receptor V-set domains. CD28 is expressed constitutively on almost all human CD4 T cells and approximately 50% of CD8 T cells. CD28 costimulation has diverse effects on T cell function, including biochemical events at the immunological synapse, downstream phosphorylation and other post-translational modifications, transcriptional changes, and cytoskeletal remodeling. At the most basic level, CD28 signals increase a cell’s glycolytic rate, allowing cells to generate the energy necessary for growth and proliferation.
| Z03413 | |
|
|
|
| ¥27,981.00 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ask us a question | |